
Lost?
Pages
Labels
- Our Accomplishment (1)
- Our Gains (1)
- Our Mission (1)
- Our Team (1)
- Overview (1)
Blog Archive
Followers
Follow the leader of this group!!! XD
We will learn how to use a universal tensile testing machine to conduct tests on distinct class of materials, such as a common polymeric materials (Polyethylene Terephtalate, PET), high performance Kevlar fibers, and a light-weight aluminium alloy. We will analyze the data, extract the critical properties, and discuss them for each class of materials.
(B) Scanning Electron Microscope
The main objective of this activity is to get familiar with the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and the most common detectors used to collect images and chemical data of materials.
The objectives will be a basic understanding and assimilation of the following:
1) Basics of Scanning Electron Microscopy theory and instrumentation
2) Basics of Signal Detection theory and instrumentation for Secondary Electrons (SE), Backscattered Electrons (BSE) and Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) detectors.
Outcome: To learn about scanning electron microscope through the use of stimulations
We will learn about the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) which is an important and routine tool in materials science. The SEM allows for visualization of topographical as well as chemical contrasts of materials at the sub-micron scale. We will understand electron/matter interactions and how such interactions are exploited to create images of materials surfaces. The physical principles of SEM operation, including generation of electron, magnetic lenses, and detector, will be introduced. We will have access to a virtual SEM which allows them to learn the operation principles of scanning electron microscopy without any risk of equipment damage.
(C) Composite Material Processing
The objective for this experiment is to introduce materials processing to the students. In this case, it is in composite materials.
1) To understand what is composite materials and how to fabricate them
2) To appreciate the applications of composite materials in daily life
3) To appreciate the mechanical properties of composites
We are supposed to create a Blog, Report and Presentation Slides on the things that we learnt.



Thickness | Width | Gauge Length (Before) | Gauge Length (After) | |
Units | mm | mm | mm | mm |
Yellow | 4.0400 | 10.0600 | 110.7900 | 11.7000 |
Transparent | 4.0600 | 10.3500 | 114.3600 | 13.5000 |
Metal | 2.0100 | 10.0100 | 103.4000 | 11.1000 |
Name | Max force | Max distance |
Units | kN | mm |
Yellow | 0.42141 | 89.0510 |
Transparent | 1.35438 | 1.91500 |
Metal | 4.65681 | 6.77500 |



Questions to answer:
Bonus) Compare the break surface of 3 samples, and guess the relationship between ductility and break surface.
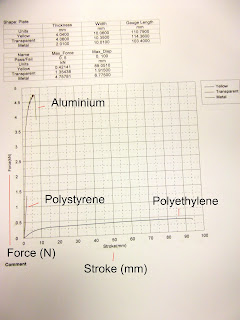
The more ductile a material is, the larger value of strain it has upon fracture. A brittle material undergoes little or no plastic deformation upon fracture compared to a ductile material. The more ductile a material is, after fracture, the more uneven the break surface will be. The more brittle a material is, after fracture, the more even and flat the break surface will be.
1) Why are there variations in mechanical properties of materials of the same type?
Even though materials are made up of the same elements or type, the bonding of elements, microstructures and molecular structure varies between different materials of the same type. An example is polyethylene and polystyrene. They are both polymers, but polyethylene is more ductile compared to polystyrene.
2) What difference exists in mechanical properties of different materials?
Ductility: Polyethylene is the most ductile, followed by aluminum copper alloy and polystyrene.
Toughness: The more the area from the start to the breaking point of the graph, the more tough the material is. Both aluminum copper alloy and polyethylene have the highest toughness, followed by polystyrene.
3) What is the major difference between polymer and metals in terms of mechanical behaviour?
Metals are usually more brittle, where the material stretches and elongates less compared to other materials. On the other hand, Polymers have a wide range of different properties, depending on the bonding of elements and microstructures of it.







2) Why is it necessary to stir and mix the epoxy and hardener solution for quite a long time?
Both solutions are viscous and thick, which makes them harder to mix evenly. Also, epoxy requires the mixture of hardener solution with to be working at its optimal level. Thus, it is crucial to stir and mix it well for the layers of carbon/glass fiber to stick well.
3) Why are most materials are only made up of 30-40% of composite materials?
Composite materials are known for their strong and hard properties, thus, it makes it brittle and some applications of the airplane wings, which have to be a bit flexible, or it will be easily destroyed in pressure/resistance.
