This section will include tables of data, observation and findings, as well as questions regarding the projects.
(A) Tensile Testing of Engineering Materials
Tables of data:
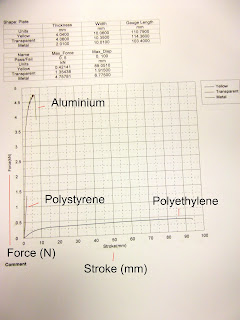
Above is a picture taken of the data. The tables are typedbelow; The graph shows the line of three material samples, the aluminum sample (Grey), polystyrene sample (Transparent) and polyethylene sample (Yellow).
| Thickness | Width | Gauge Length (Before) | Gauge Length (After) |
Units | mm | mm | mm | mm |
Yellow | 4.0400 | 10.0600 | 110.7900 | 11.7000 |
Transparent | 4.0600 | 10.3500 | 114.3600 | 13.5000 |
Metal | 2.0100 | 10.0100 | 103.4000 | 11.1000 |
Name | Max force | Max distance |
Units | kN | mm |
Yellow | 0.42141 | 89.0510 |
Transparent | 1.35438 | 1.91500 |
Metal | 4.65681 | 6.77500 |
Analysis of results (Table and graph):
Polyethylene material (Yellow): Plastic deformation under fracture; High strain; breaking point was soon after reaching the Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS).
Break surface: Stretched and elongated. Thus we can conclude that it is ductile.
Polystyrene material (Transparent): Little elongation and plastic deformation can be found upon fracture; Low strain; Broke at the UTS.
Break surface: clean and flat. Thus we can conclude that it is brittle.

Aluminium-copper alloy (Metallic): Some plastic deformations upon fracture; Low strain; Broke shortly after reaching UTS.
Break surface: Slightly stretched and elongated. Because so, we conclude that it is in between brittle and ductile, but more towards brittle.
Questions to answer:
Bonus) Compare the break surface of 3 samples, and guess the relationship between ductility and break surface.
The more ductile a material is, the larger value of strain it has upon fracture. A brittle material undergoes little or no plastic deformation upon fracture compared to a ductile material. The more ductile a material is, after fracture, the more uneven the break surface will be. The more brittle a material is, after fracture, the more even and flat the break surface will be.
1) Why are there variations in mechanical properties of materials of the same type?
Even though materials are made up of the same elements or type, the bonding of elements, microstructures and molecular structure varies between different materials of the same type. An example is polyethylene and polystyrene. They are both polymers, but polyethylene is more ductile compared to polystyrene.
2) What difference exists in mechanical properties of different materials?
Ductility: Polyethylene is the most ductile, followed by aluminum copper alloy and polystyrene.
Toughness: The more the area from the start to the breaking point of the graph, the more tough the material is. Both aluminum copper alloy and polyethylene have the highest toughness, followed by polystyrene.
3) What is the major difference between polymer and metals in terms of mechanical behaviour?
Metals are usually more brittle, where the material stretches and elongates less compared to other materials. On the other hand, Polymers have a wide range of different properties, depending on the bonding of elements and microstructures of it.
(B) Scanning Electron Microscope
Tables of data (Titania):

The picture shows data taken from Titania when doing area analysis in EDS/EDX, which is used to detect chemical compounds.
Tables of data (Carbon Nano-tube):
The data on the left shows a graph of the different chemical compounds in a part of the Carbon Nano-tube. The data on the right shows the percentage of elements found in that area.
Tables of data (Solder):
The data on the left shows the overall picture of the Solder, and different points can be selected. The data on the right shows the chemical composition at the +001 point.
Tables of data (Srilankite):
The data on the left shows the overall scan of the Srilankite, where like in the Solder, different points can be selected. The data on the right shows the chemical composition and other data at the +002 point.
Questions to answer:
1) What do you think may be caused if there is too much moisture on the specimen?
If there is too much moisture on the specimen, when the electron gun fires on the specimen plate, the readings might be inaccurate as they might come from the water content instead of the specimen.
Backscattered electrons might not be produced or detected.
2) What is the working distance and accelerate voltage if the specimen is titanium?
If the specimen is titanium, the accelerate voltage is 10-15kV and the working distance is 10 mm.
3) Why can't we heat the filament too fast?
It will blow and break prematurely.
(C) Composite Material Processing
Logsheet (Calculations taken during the experiment):
Weight of fiber matt (Calculated from epoxy required): 30 / 62.5% = 4.8g
Weight of fiber matt (Calculated from hardener s
olution required): 20 / 37.5% = 5.3g
Average/Total weight of fiber matt used = 4.8 + 5.3 / 2 = 5.1g
Weight of epoxy required = 30g
Weight of hardener solution required = 20g
Question created by us to answer:
1) Why is the teflon sheet, plastic sheet and tissue paper needed to be above and below the fiber and epoxy?
Teflon sheet is used because it is hard for epoxy to pass through it, thus the epoxy would not mess up the work space. Tissue paper and plastic sheet, we believe, is used for extra protection in case the epoxy goes through the teflon layer.
2) Why is it necessary to stir and mix the epoxy and hardener solution for quite a long time?
Both solutions are viscous and thick, which makes them harder to mix evenly. Also, epoxy requires the mixture of hardener solution with to be working at its optimal level. Thus, it is crucial to stir and mix it well for the layers of carbon/glass fiber to stick well.
3) Why are most materials are only made up of 30-40% of composite materials?
Composite materials are known for their strong and hard properties, thus, it makes it brittle and some applications of the airplane wings, which have to be a bit flexible, or it will be easily destroyed in pressure/resistance.